Utilizing Mind Mapping Techniques to Improve Knowledge Retention in Self-Directed Learning
Understanding the Power of Mind Mapping
In an era where information is at our fingertips, the challenge of retaining knowledge has become increasingly significant. Self-directed learners, from high school students to working professionals, often find themselves inundated with information, making it difficult to remember what they have learned. This is where mind mapping techniques come into play as an innovative solution for enhancing memory retention.
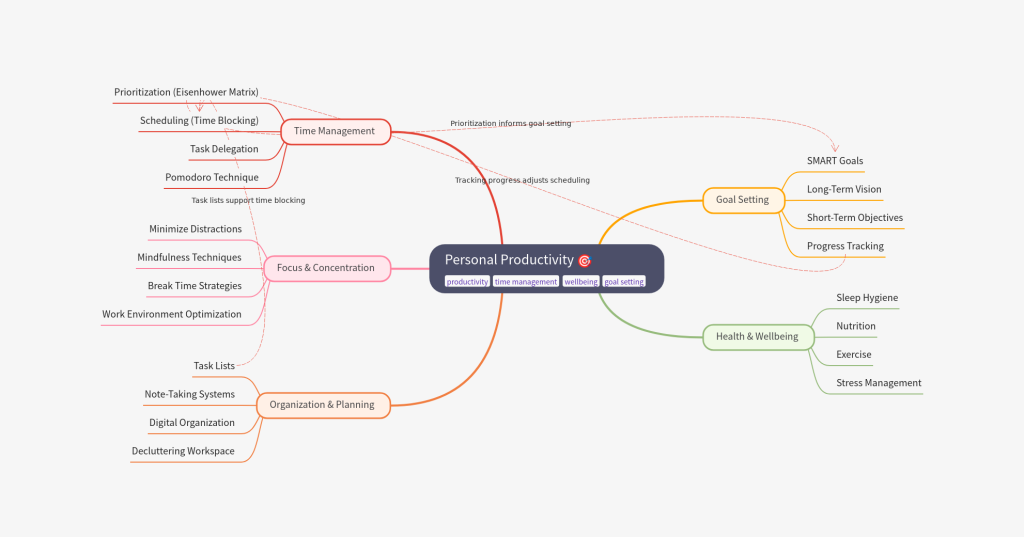
Mind mapping is more than just a study tool; it’s a visual thinking strategy that allows individuals to organize their thoughts and ideas effectively. By using colors, images, and branching structures, learners can create a vibrant map that captures the essence of their study material. Here’s how mind mapping can enrich the learning experience:
- Visualizing Ideas: The human brain is wired to process visual information better than text. By organizing information visually, learners can identify and comprehend relationships between concepts, which aids in understanding.
- Encouraging Engagement: The interactive nature of mind mapping fosters a more active learning environment. For example, students can collaborate on a mind map for a group project, making the process enjoyable and reinforcing their memories through shared ideas.
- Facilitating Recall: The hierarchical structure of a mind map makes information more digestible. Instead of drowning in a sea of notes, learners can glance at their map and quickly retrieve the details they need, reducing anxiety over exams or presentations.
Numerous studies have highlighted the effectiveness of visual learning aids in boosting information retention. For instance, research indicates that individuals are likely to remember 80% of information presented visually, compared to just 20% of what they read. Moreover, a combination of seeing and doing—such as using colors or drawings in mind maps—can improve retention to around 60%.
As self-directed learners seek ways to optimize their studies, mind mapping stands out as a particularly effective strategy. This technique not only transforms complex information into manageable formats but also cultivates a deeper understanding and enhanced confidence in one’s learning process. Imagine tackling an entire semester’s worth of study material by creating mind maps for each subject; not only does this make study time more engaging, but it also prepares learners to recall information with assurance when it matters most.
In conclusion, utilizing mind mapping can be an invaluable asset in the realm of self-directed learning. By embracing this dynamic approach, learners can effectively navigate the overwhelming amount of information presented to them daily, ensuring that they maximize their educational outcomes. Implementing mind maps could very well be the key to unlocking stronger memory skills and overall academic success.
DIVE DEEPER: Click here to unlock the secrets of self-discipline
Unpacking the Components of Effective Mind Mapping
The success of mind mapping techniques in enhancing knowledge retention hinges on several key components. Understanding these elements can empower self-directed learners to leverage mind maps more effectively in their educational pursuits. Here are the fundamental aspects that contribute to the efficacy of mind mapping:
- Central Ideas: At the core of every mind map lies a central idea or theme, which serves as the focal point. This is crucial for ensuring clarity and direction. When self-directed learners define their central ideas clearly, it provides a thematic anchor that allows for better organization and comprehension of associated concepts.
- Branching Structure: Mind maps utilize a branching structure to create relationships between concepts. With main branches representing primary ideas and sub-branches diving deeper into supporting details, this hierarchical arrangement mirrors natural thought processes, promoting organic connections between concepts.
- Colors and Imagery: Engaging visual elements such as colors, icons, and images significantly enhance memory retention. By associating vibrant colors with different ideas, learners can create a visual code that facilitates quicker recognition and recall. The brain tends to remember visually striking images more than plain text, making this approach especially effective.
Incorporating these components into mind mapping for self-directed learning can vastly improve the depth of understanding and retention of the material. A study conducted by the University of California found that methods employing visual aids, such as mind maps, led to a 25% increase in information retention over notes alone. Learners who embrace this strategy often report that mind maps help them to not only remember facts but also apply their knowledge in practical settings.
Examples of applying mind mapping techniques in various educational contexts abound. For instance, high school students preparing for college entrance exams can break down complex subjects like calculus into visual representations, making it easier to identify formulas and applications. Working professionals can use mind maps to churn through information quickly during corporate training sessions, facilitating more effective learning and real-time application of new skills.
As self-directed learners increasingly turn to digital tools, software and applications have emerged that streamline the mind-mapping process. Programs like MindMeister and XMind allow users to create professional and aesthetically pleasing mind maps that can be easily edited and shared. Such tools enhance collaboration, especially for learners engaged in group projects or discussions, enriching the collective knowledge base that leads to improved retention.
Ultimately, mastering the art of mind mapping requires practice and creativity. By experimenting with different styles and structures, learners can develop a personalized approach that resonates with their unique learning preferences. This not only helps embed knowledge but also fosters a more engaging and less daunting learning experience, paving the way for long-term success.
Exploring Mind Mapping Techniques for Enhanced Learning
In the quest for improved knowledge retention in self-directed learning, mind mapping emerges as a powerful technique that transforms traditional note-taking into a dynamic, interactive experience. At its core, mind mapping allows learners to visually represent information, enhancing their ability to connect and organize concepts effectively. This technique is particularly beneficial for individuals pursuing independent study, as it not only facilitates the assimilation of new information but also encourages creativity and deeper understanding.One of the most significant advantages of employing mind mapping is its ability to mirror the way our brains work. When learners map out their ideas, they are essentially creating a graphical representation that engages both hemispheres of the brain, fostering a holistic learning experience. This fluid organization of information leads to better recall and enhances critical thinking skills, positioning learners for success in self-directed educational pathways.Moreover, mind mapping provides structure in chaotic learning environments, helping individuals break down complex topics into digestible chunks. By categorizing information visually, learners can easily identify relationships and hierarchies within concepts, making it simpler to grasp intricate subjects. The visual nature of mind maps aids in the encoding process, ensuring memories are stronger and more easily retrievable during assessments or practical applications.Encouraged by the efficacy of mind mapping, many educators and learners are incorporating digital tools that offer templates and customization options. These innovations not only enhance engagement but also allow for easy modifications, ensuring that learning remains flexible and adaptive to individual needs. As we further explore the benefits of mind mapping, it becomes evident that this technique is not just a passing trend but rather a foundational skill that can redefine self-directed learning. By embracing this method, learners can unlock their potential, transforming information into actionable knowledge that lasts.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Visual Learning | Mind mapping utilizes graphics to enhance comprehension and retention. |
| Engagement | Interactive and creative approach fosters a deeper connection to the material. |
By understanding the advantages of mind mapping, learners can take significant strides towards mastering their subject matter and achieving their educational goals.
DIVE DEEPER: Click here to learn more about simulation and role-playing techniques
Enhancing Engagement through Collaborative Mind Mapping
Collaboration is a vital aspect of the learning process, and mind mapping techniques naturally lend themselves to group engagement. When self-directed learners come together to create mind maps, they can tap into a wealth of diverse perspectives, fostering a richer educational experience. Collaborative mind mapping not only sharpens critical thinking but also promotes discussion and debate, which are essential for deeper understanding.
In educational settings, using collaborative mind mapping tools like Miro or Padlet can help groups brainstorm ideas effectively. For example, a group of college students assigned to work on a research project can utilize these platforms to collectively develop a mind map. This not only enhances the organization of their thoughts but allows each member to contribute unique insights. The resulting visual representation serves as a powerful study guide, capturing the essence of their discussion and providing a reference point that aids retention.
Research indicates that when students actively engage in learning through group dynamics, knowledge retention improves. A meta-analysis published in the Journal of Educational Psychology suggests that collaborative learning approaches, which include group mind mapping, can lead to a 40% increase in retention rates compared to solitary study methods. This underscores the value of creating communal spaces for learning, where ideas can be shared and built upon.
Catering to Different Learning Styles
The versatility of mind mapping techniques also allows them to cater to various learning styles. David Kolb’s Experiential Learning Theory emphasizes that individuals learn differently—some through visual means, while others may prefer auditory or kinesthetic approaches. Mind mapping serves as a bridge that accommodates these differences by providing a multi-sensory learning experience.
For visual learners, the use of colors, images, and visual hierarchies in mind maps translates complex information into easily digestible formats. On the other hand, auditory learners can benefit from discussing mind maps aloud, reinforcing their understanding through verbal articulation. Kinesthetic learners may incorporate physical elements into their mind maps by using sticky notes or tactile materials to create a three-dimensional representation of their thoughts.
This adaptability makes mind mapping an inclusive tool that can resonate with a diverse audience, ensuring that all learners can enhance their knowledge retention effectively. Additionally, educators can use mind mapping as a diagnostic tool to identify students’ preferred learning styles, allowing them to tailor instructions accordingly.
Assessment and Revision with Mind Mapping
Another compelling application of mind mapping techniques is in the assessment process. By revisiting and revising mind maps, learners can reinforce their grasp of a subject matter over time. Regularly updating a mind map as new information is absorbed not only solidifies previous knowledge but also encourages the integration of concepts into a coherent framework. For instance, medical students often utilize mind maps to revise complex subjects like human anatomy; by continually revising and adding to their maps, they keep information fresh and interrelated.
Furthermore, incorporating reviews through mind mapping helps with long-term retention. A study from the University of Maryland found that students who regularly revise their material using mind maps experienced fewer knowledge decay rates compared to those relying solely on traditional notes. This practice aids learners in linking concepts over time, leading to more profound retention of knowledge.
By utilizing mind mapping techniques in these ways, self-directed learners can further enhance their engagement and retention capabilities. As this trend continues to shape educational practices, it illuminates the potential of mind mapping as not just a tool for organization but a powerful strategy to maximize learning outcomes.
DIVE DEEPER: Click here to uncover the link between emotional engagement and skill retention</
Conclusion: Empowering Self-Directed Learning Through Mind Mapping
In an increasingly complex educational landscape, utilizing mind mapping techniques emerges as a transformative approach to enhance knowledge retention among self-directed learners. By enabling individuals to visualize their thoughts and connections, mind maps effectively break down intricate subjects into manageable, organized formats. The blend of creativity and structure inherent in mind mapping nurtures not only individual comprehension but also collaborative dynamics, where diverse insights fuel deeper understanding.
As highlighted throughout this article, the adaptability of mind mapping caters to varying learning styles, making it a universal tool suited for a broad audience. Whether one is a visual, auditory, or kinesthetic learner, mind maps offer an inclusive learning experience that promotes active engagement. By encouraging continuous assessment and revision, learners can reinforce their understanding and minimize knowledge decay. This is particularly evident when students engage with subjects that require critical thinking and integration of complex concepts.
Moreover, the effectiveness of collaborative mind mapping in group settings not only enhances retention rates but also builds essential soft skills, such as teamwork and communication. The substantial improvement in learning outcomes is supported by empirical research, suggesting that mind mapping could lead to retention increases of up to 40% compared to conventional study methods.
In conclusion, mind mapping transcends its role as merely a visual tool; it stands as a comprehensive strategy poised to revolutionize self-directed learning. By integrating this technique into daily study habits or educational curricula, learners can unlock their potential for greater comprehension and retention, ultimately navigating their educational journeys with clarity and confidence.


